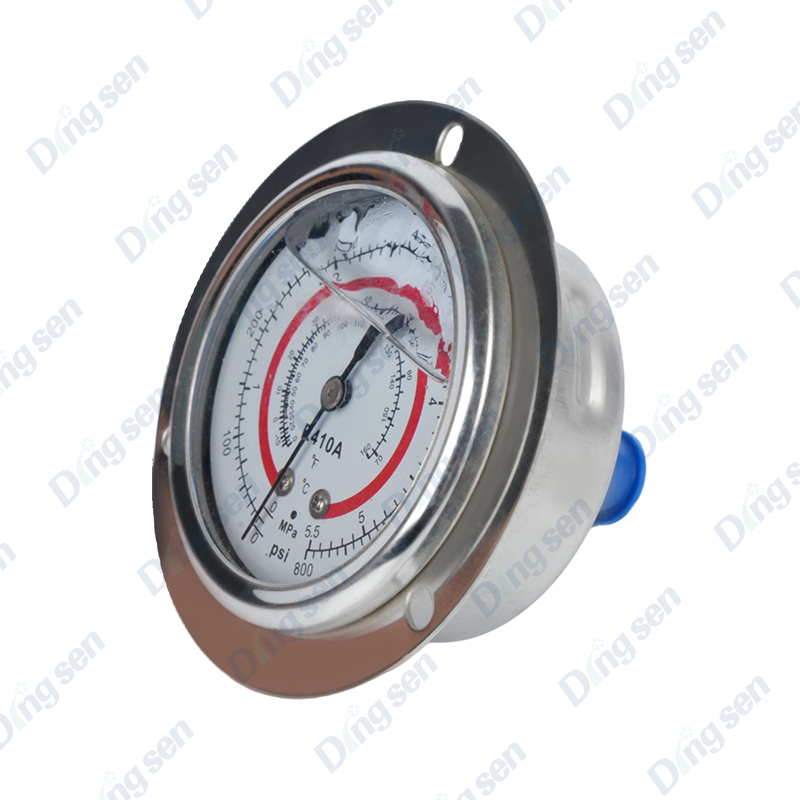
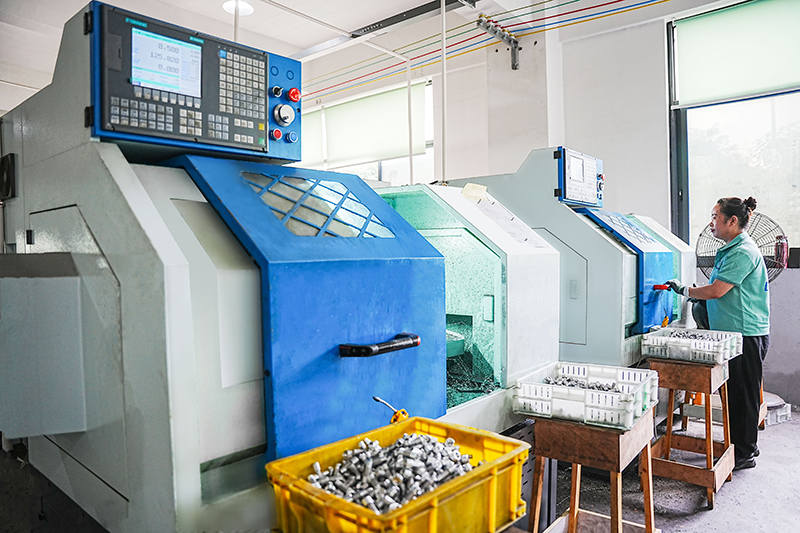
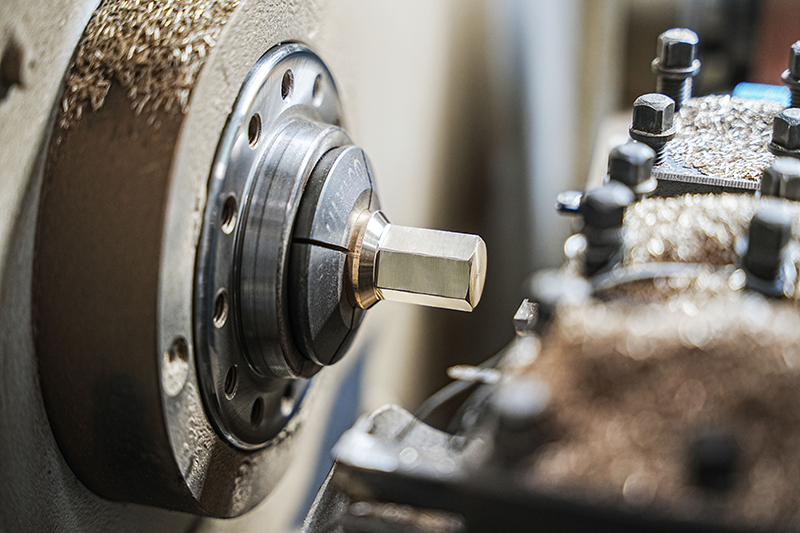
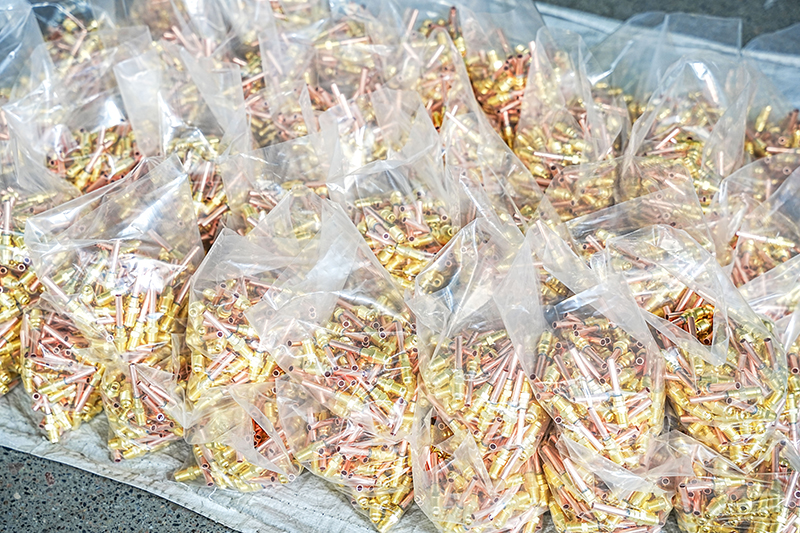
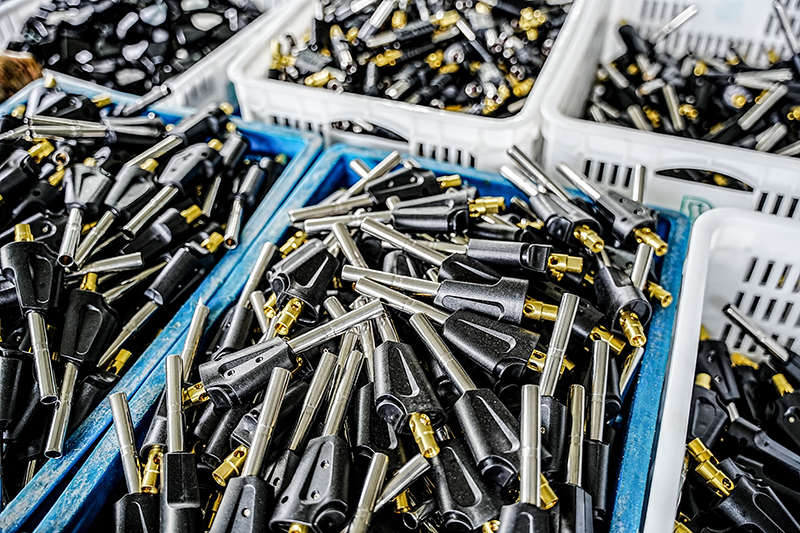
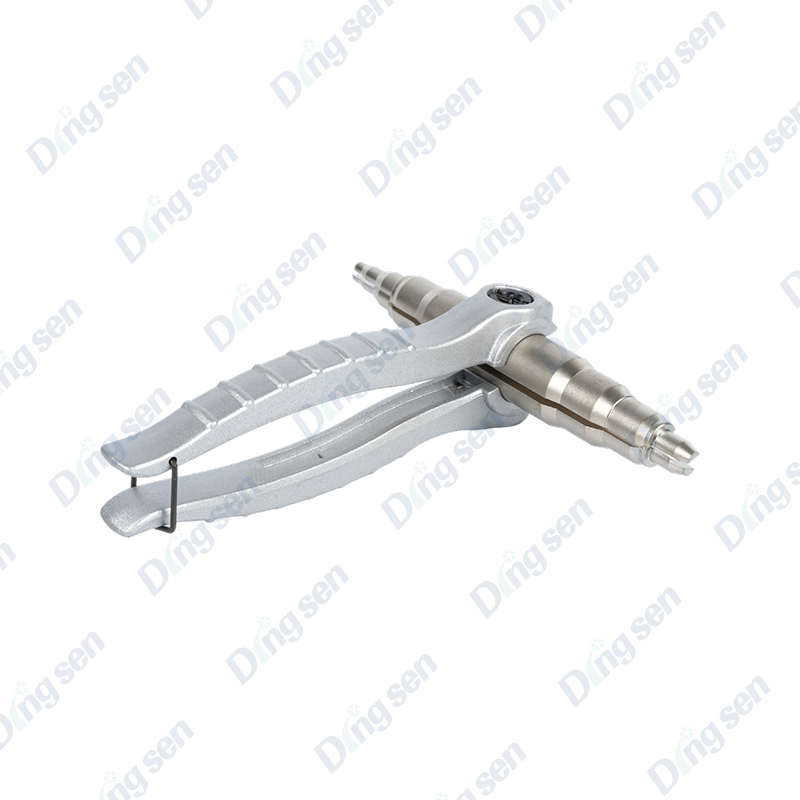
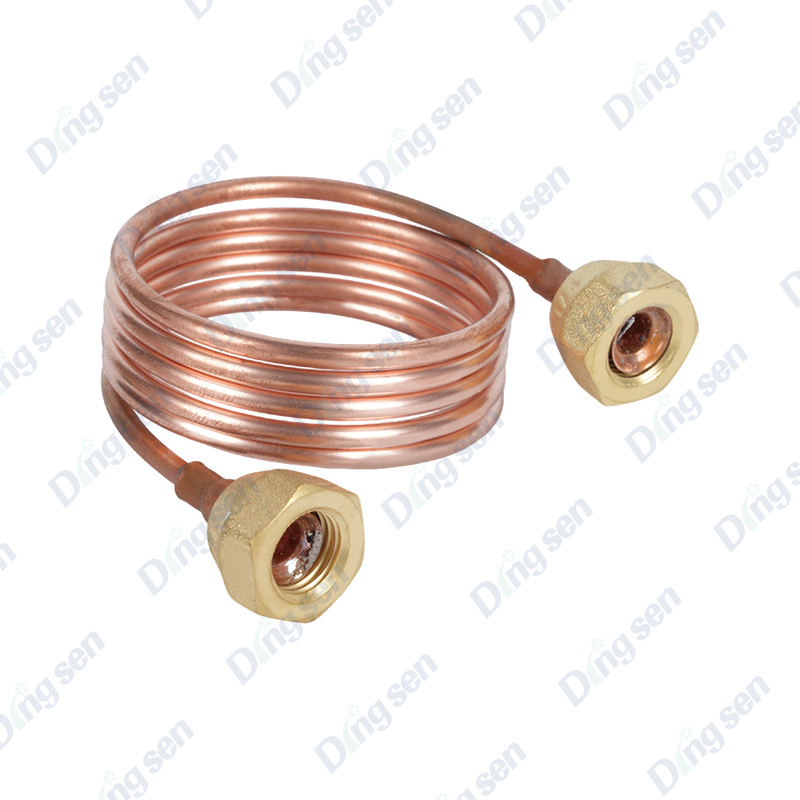
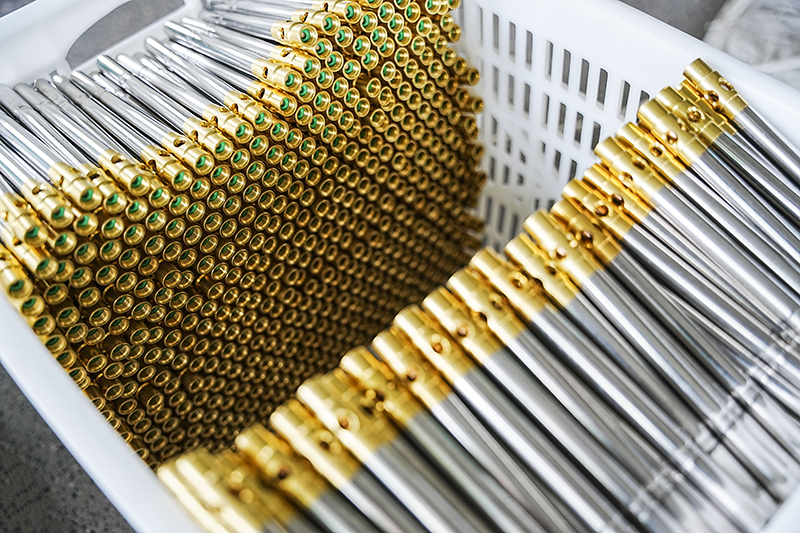
In air conditioner installation and maintenance, the differences between thickened air conditioner nuts and ordinary nuts are very significant, mainly in terms of pressure resistance, sealing stability, and crack resistance. Ordinary nuts have thinner walls and are prone to micro-cracks under high p...
READ MORECopper Branch pipe series
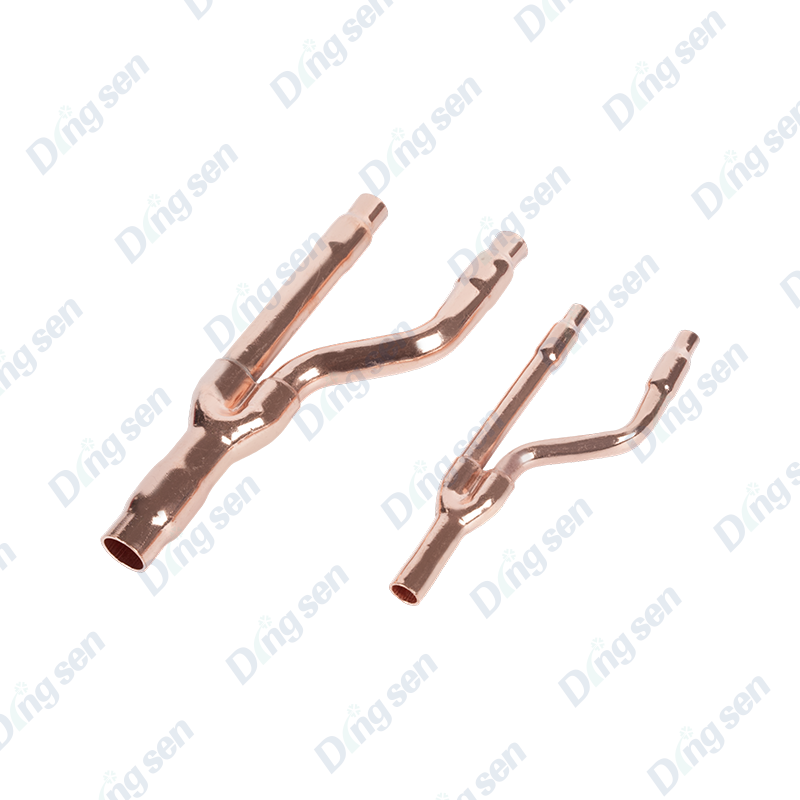
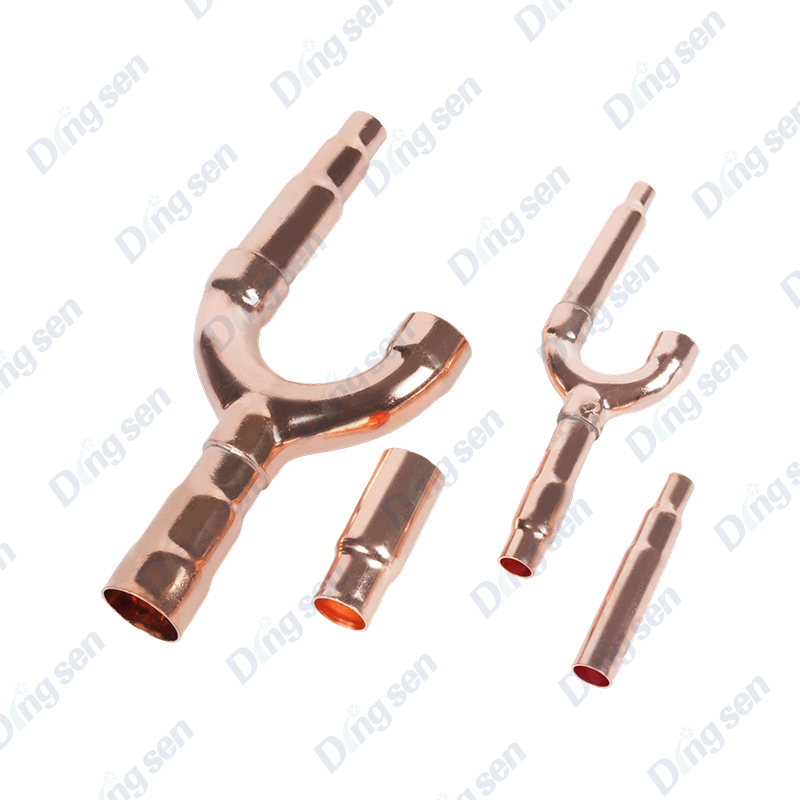
Copper Branch pipe series are core components for refrigerant distribution in refrigeration systems. They evenly distribute refrigerant to multiple branches, ensuring efficient coordination between multiple heat exchange units and adapting to various types of refrigeration equipment.
They are used for refrigerant distribution in multi-split central air conditioning systems, cold storage, and commercial refrigeration systems.
Produced with premium copper, they undergo precision forging and pressure testing, ensuring compatibility with mainstream refrigerants and excellent sealing.
Our service includes selection and installation guidance. Advantages include uniform flow distribution, strong corrosion resistance, excellent thermal conductivity, and stable operation. Copper manifolds are core components for efficient refrigerant distribution in refrigeration systems. Their key advantages are "precise flow distribution and strong environmental adaptability." Crafted from precision-forged copper, they feature a fluidically optimized manifold cavity. Equipped with 2-6 equal-diameter or reducing-diameter branch ports, they evenly distribute gaseous or liquid refrigerant to each branch, ensuring consistent cooling efficiency across multiple heat exchange units (such as VRF indoor units and cold storage evaporators). They withstand extreme operating temperatures of -200°C to 250°C and a working pressure of 3.2 MPa. They are compatible with mainstream refrigerants such as R22, R410A, and R32, and exhibit excellent corrosion resistance in humid environments. The branch ports are precision-turned to a 6H-grade thread accuracy. Select models feature built-in filters to filter refrigerant impurities and prevent branch clogging. Customizable branch counts (2-8) and port diameters (6mm to 28mm) are supported to accommodate diverse system designs. External welded locating rings facilitate precise alignment during installation, minimizing welding deviations. Applications include commercial central air-conditioning multi-split systems (refrigerant distribution between outdoor units and multiple indoor units), large cold storage (refrigerant supply for multiple evaporators), commercial refrigerator clusters (unified refrigerant delivery for multiple display cabinets), and industrial refrigeration systems (such as multi-branch heat exchange for chemical cooling equipment). Whether it is the core diversion configuration when building a new system or the upgrade of diversion components in old equipment, stable diversion can avoid local cooling shortages or energy waste. At the same time, the high ductility of copper facilitates adaptation to complex piping layouts, improving the operational stability and energy efficiency of the overall refrigeration system.
-
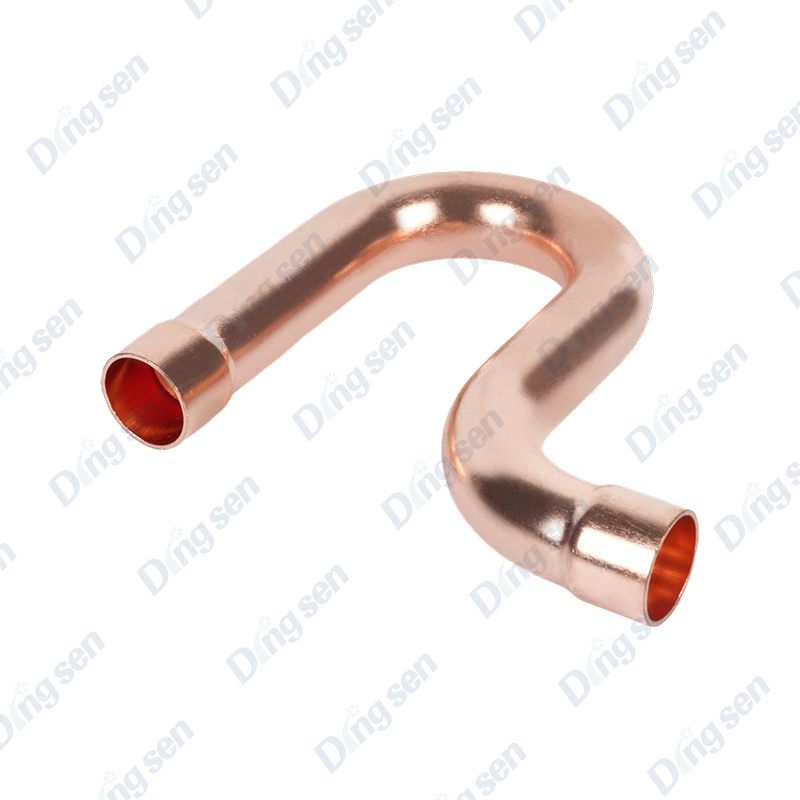
Copper pipe fittings are core connectors for air conditioning and refrigeration ...
-
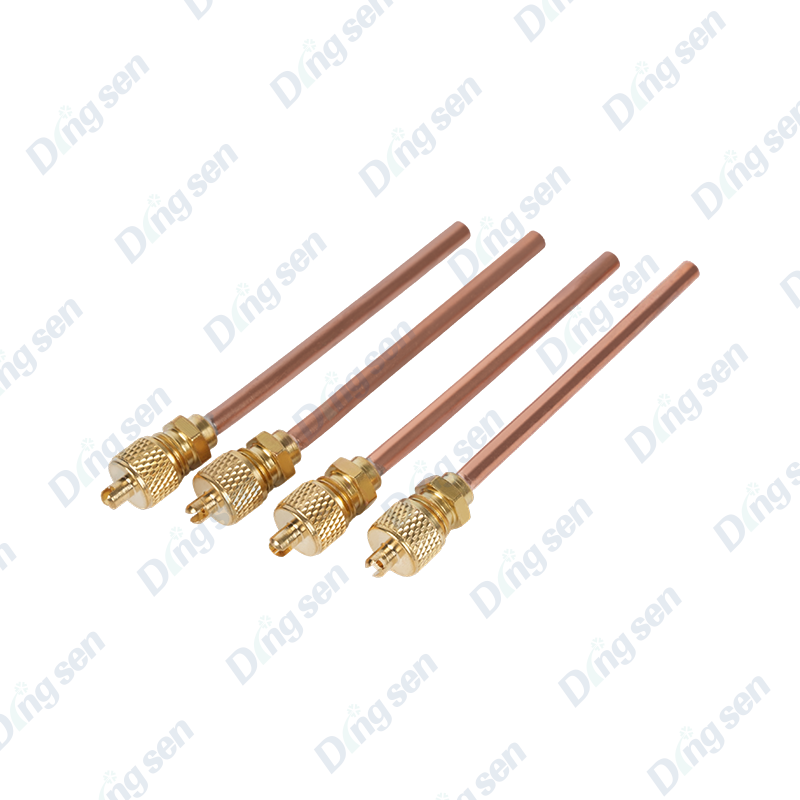
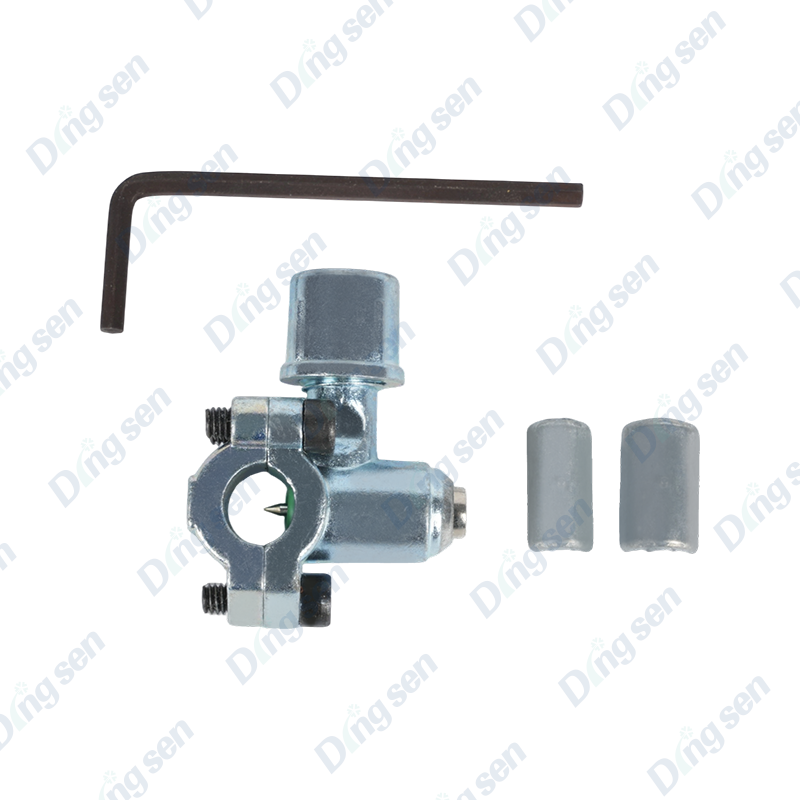
The copper pipe puncture valve is a specialized valve for copper pipe system mai...
-
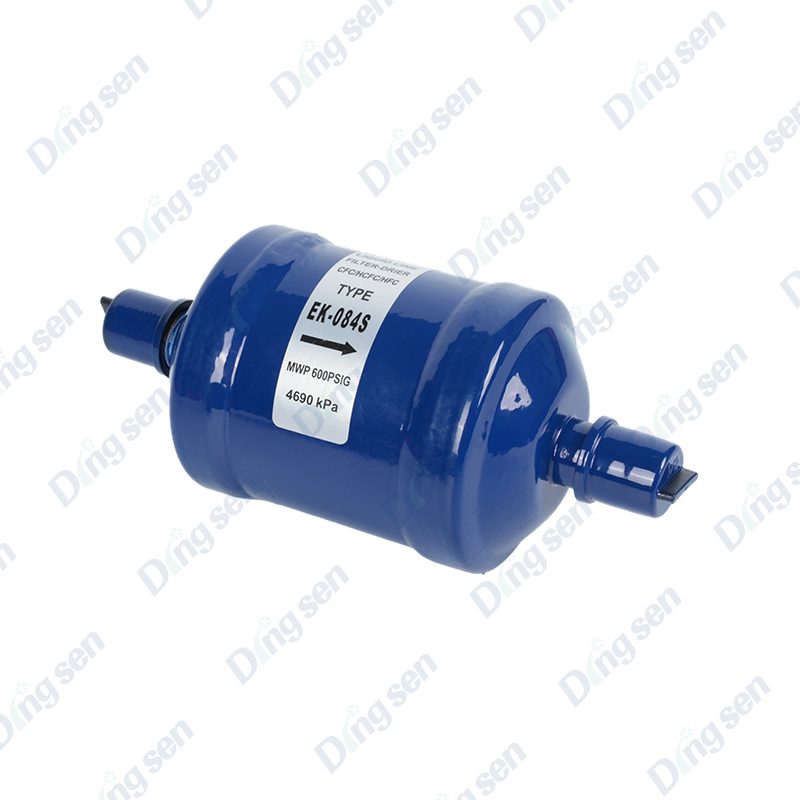
The copper drying filter is a specialized purification component for refrigerati...
-
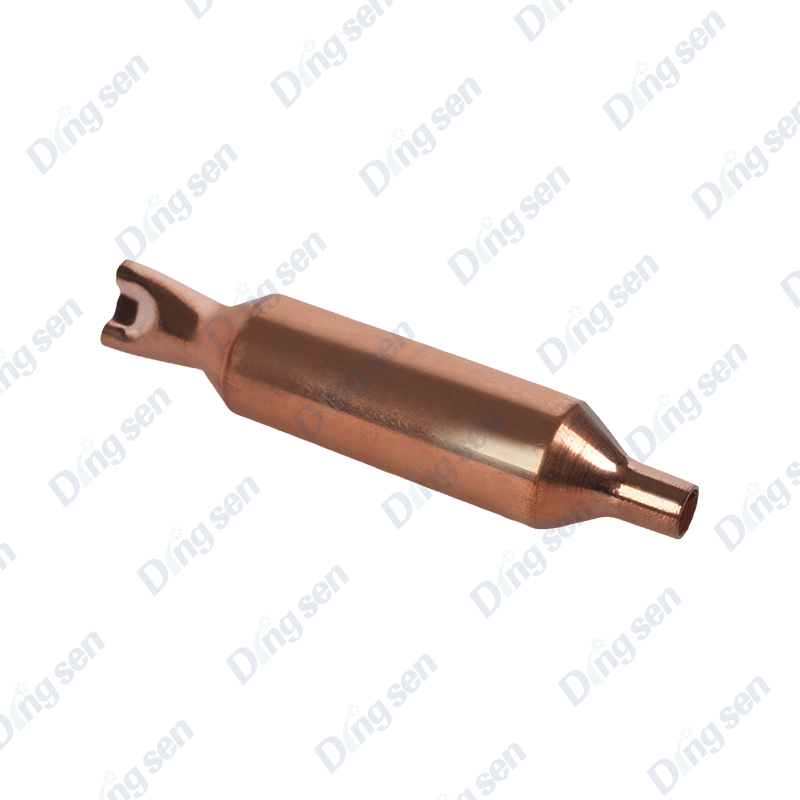
The copper tube expander is a specialized tool for copper tube connection. It ex...
-
Copper capillary tube assemblies are core throttling components in refrigeration...
-
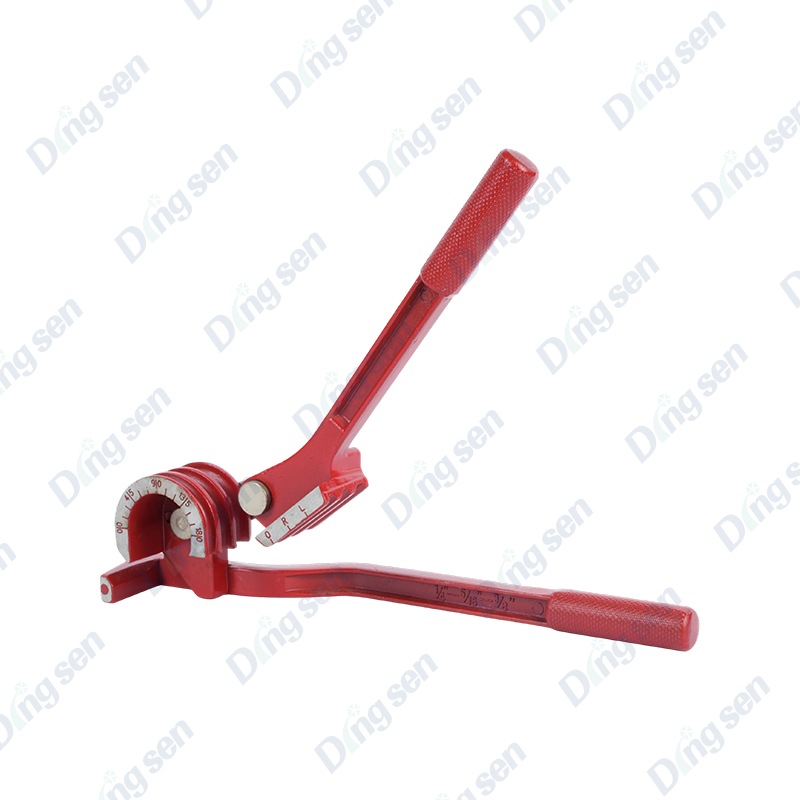
A copper tube bender is a specialized tool for forming copper tubes. It bends co...
About DingSen
- Dingsen: Refrigeration & auto AC parts since 2008.
- Decades of precision manufacturing.
- Durable evaporators, condensers, connectors.

shaoxing DingSen Refrigeration Technology Co Ltd.
-
-
A cylinder valve, as a key pneumatic control component, operates on the principle of compressed air power conversion. Simply put, a cylinder valve controls the inflow and outflow of compressed air to drive the linear or rotary motion of a piston within the cylinder, thereby automating the operation ...
READ MORE -
Charging air conditioner refrigerant using a Fluorine filling hose involves four core steps: First, connect the Fluorine filling hose to the pressure gauge manifold and the refrigerant cylinder; second, purge the air from the hose (evacuate the system); next, tightly connect the other end of the Flu...
READ MORE

 en
en  Español
Español عربى
عربى